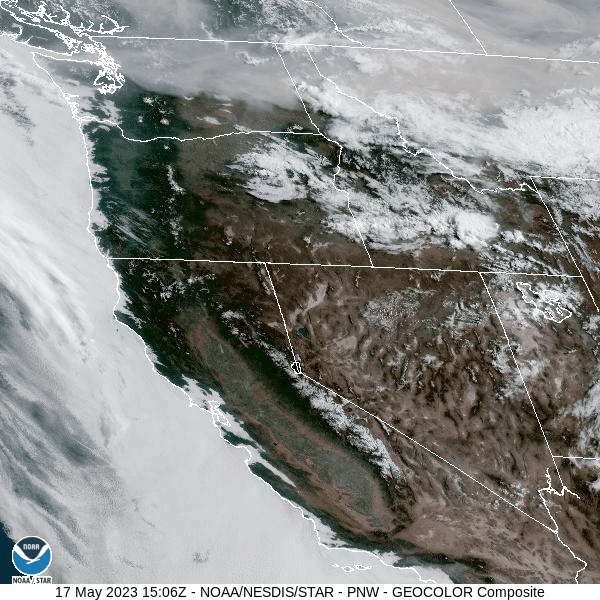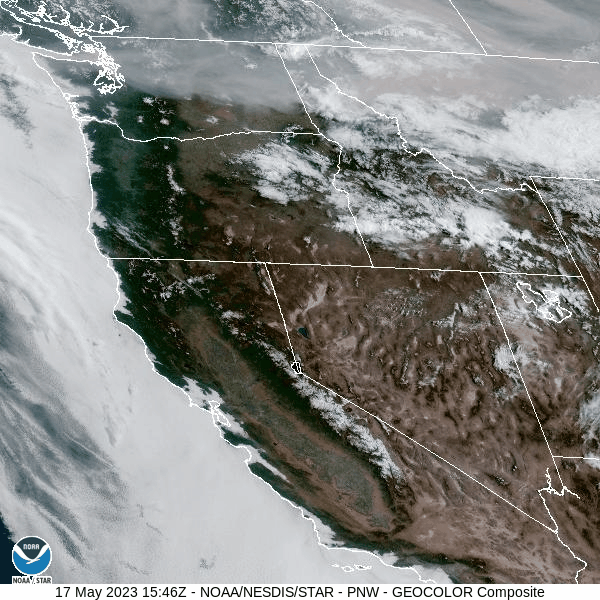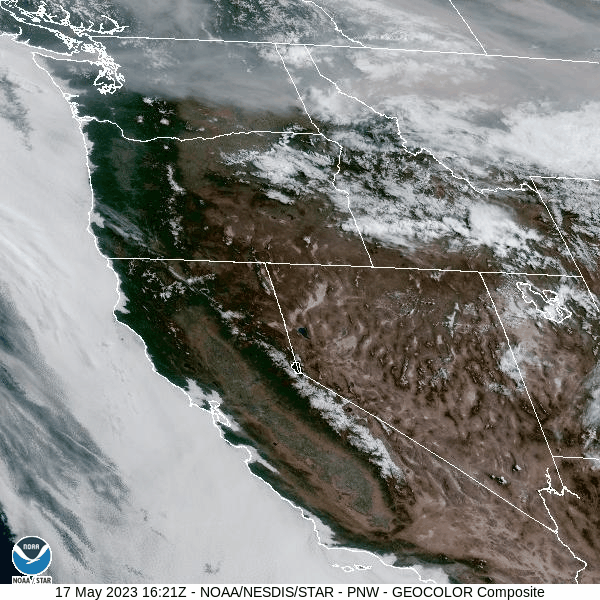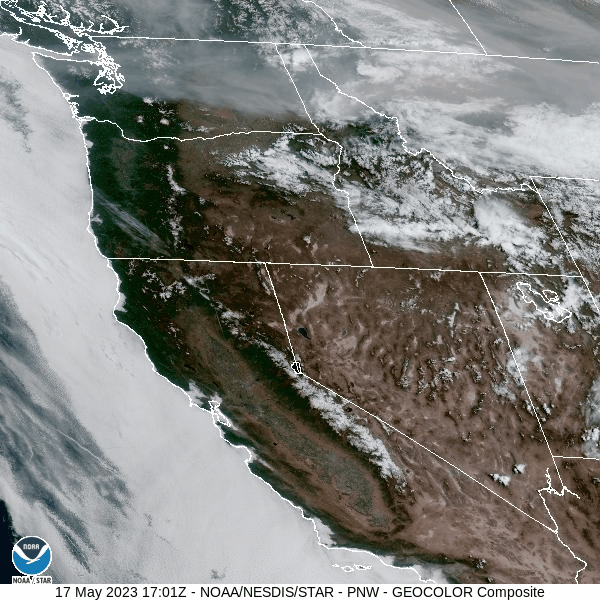
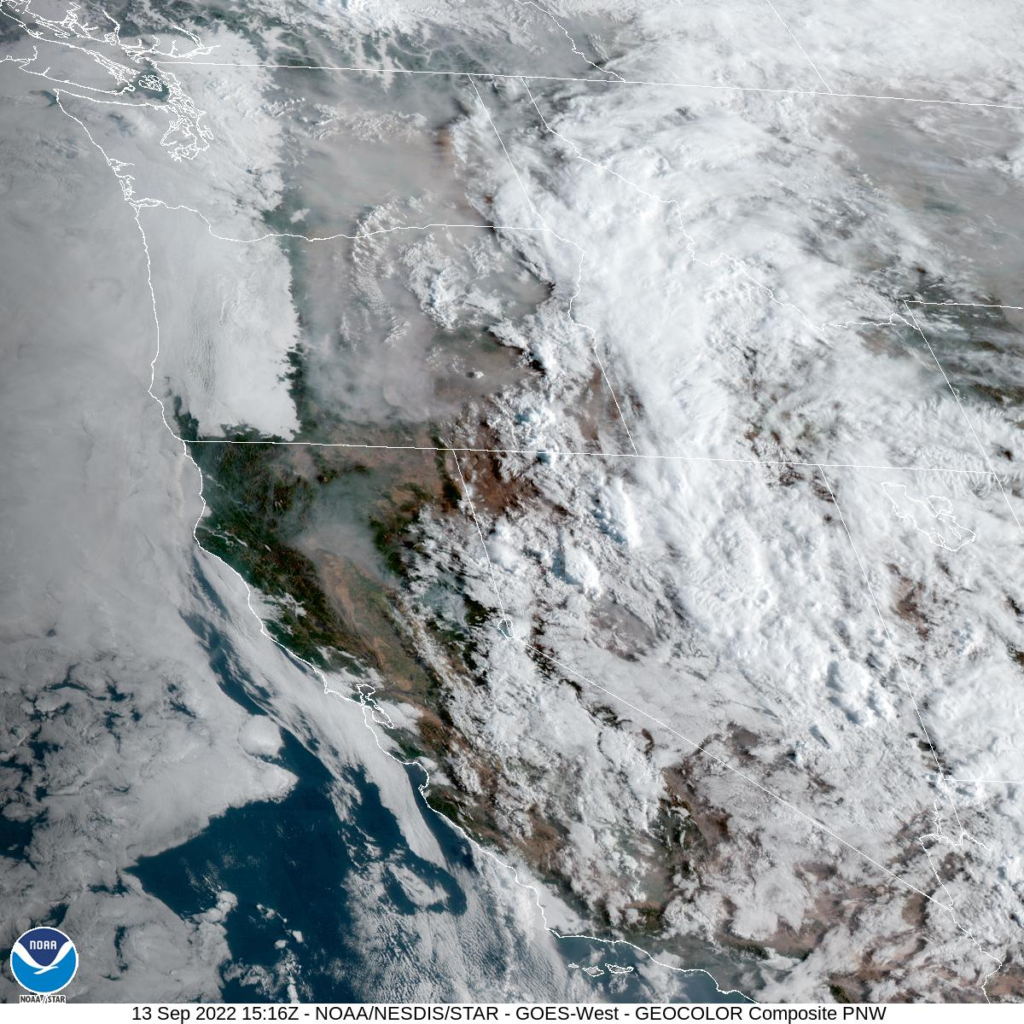
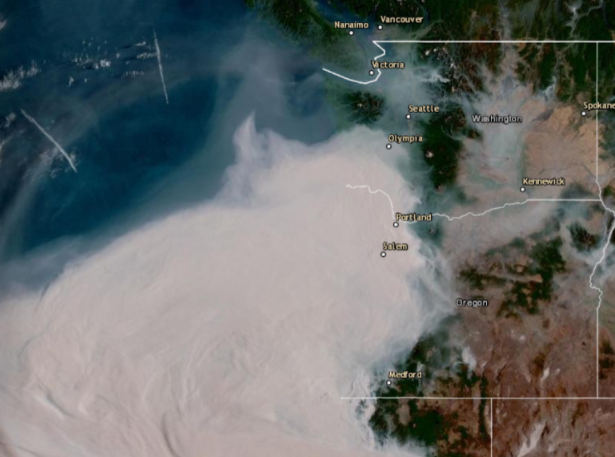
Out of Hospital Cardiac Arrests (OHCA) and Wildfire-Related Particulate Matter
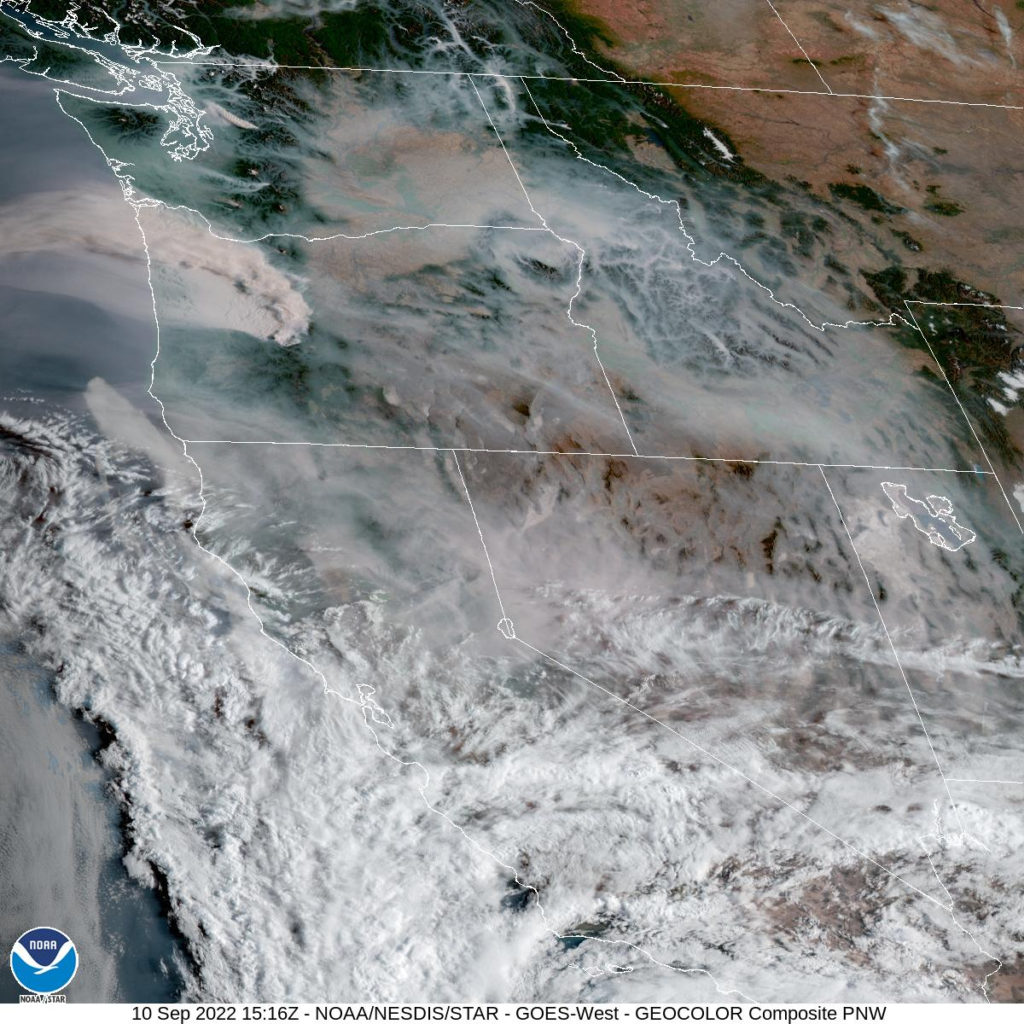
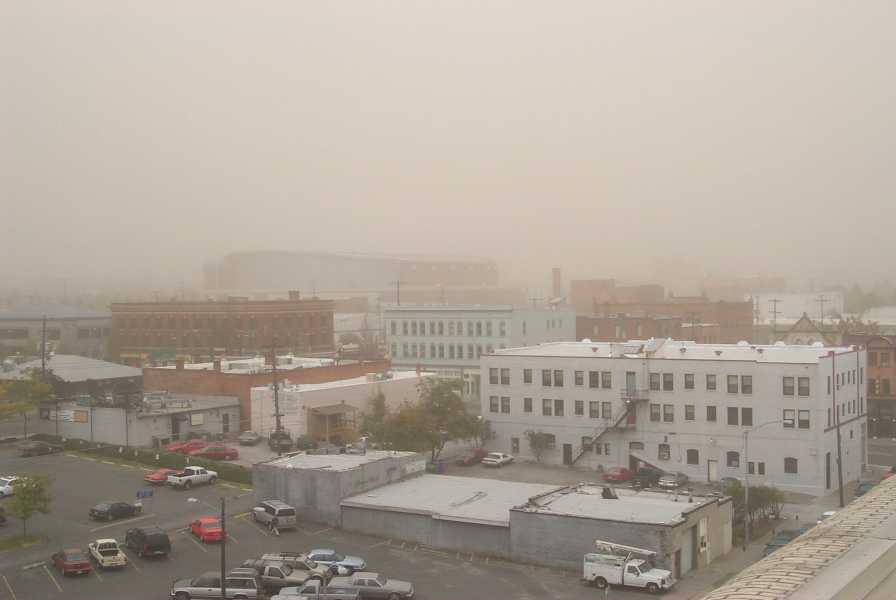
A publication by Center for Public Health and Environmental Assessment’s Ana Rappold and Wayne Cascio titled , “Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrests and Wildfire-Related Particulate Matter (PM2.5) during 2015-2017 California Wildfires,” and a complimentary press release were published by the Journal of American Heart Association (JAHA) last week. Co-authors for this study include the California Department of Public Health and Emory University. This study addresses the impact of wildfire-related fine particulate matter (or PM2.5) on out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and how the relationship between them effects age, sex, and socioeconomic status. This study found a relationship between wildfire smoke exposure and OHCA, and the effects appeared to be larger in communities with lower socio-economic status. The study was picked up by several media outlets including U.S. News & World Report.